DATA PIPELINE: WHAT IT IS AND HOW TO BUILD ONE FOR YOUR COMPANY
Data flows from one location to another is a vital operation in today’s data-driven business environment. Many businesses gather data for analysis. Even so, the data flow isn’t always seamless—it can be slowed down when it’s in transit from one location to another. When that happens, the dataset can become corrupt, cause latency, or create duplicates. A data pipeline can help ensure a smooth flow of information. It automates the extraction, validation, and loading of data, thereby combating latency and eliminating errors. Besides that, a data pipeline can process several data streams at one time. In this post, we’ll take a deep dive into what a data pipeline is and how you can build one for your company.
What Is a Data Pipeline?
A data pipeline is a concept that enables companies to optimize data transfer while securing it at the same time. In today’s business environment, data integration is a must to increase a business’s competitive edge and improve strategic decision-making. The critical actions that occur within data pipelines are essential to achieving this feat.
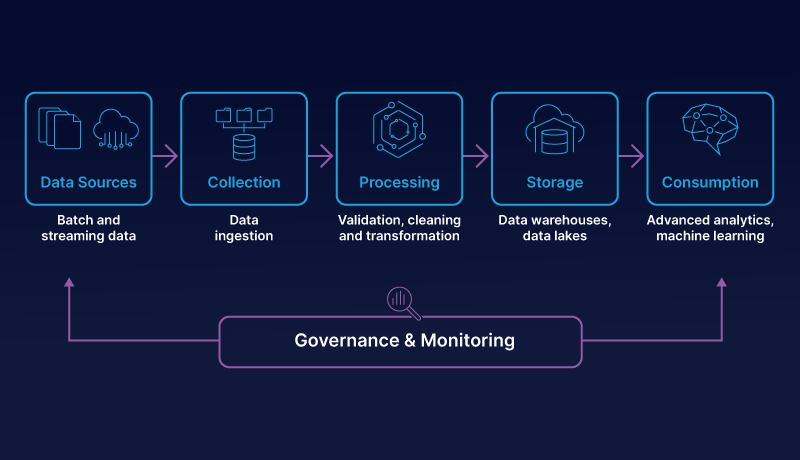
During data transfer, data is converted into a more readable form, ensuring that it arrives in a state that can be analyzed and used to develop business insights. That said, the same set of data can be used by different pipelines. For instance, a message sent to customer services can lead to:
- A report with the number of emails sent
- A report analyzing the number of words used in the message to categorize the problem
As data continues to increase at high rates, businesses are implementing data pipelines to unlock the power of their data and get the most from it.
3 Elements of Data Pipeline
Data pipelines have three key elements, namely:
- Data Collection: A company must be able to collect data from different sources, be it from file paths, Excel tables, or files. At this stage, data is neither structured nor classified, let alone processed –it is basically a data dump, and no sense can be made from it in this form.
- Data Processing: Once the data is collected, it must be organized and categorized to make it meaningful according to the context and needs of the company. Afterward, it is converted into a readable format in appropriate reports. Truncated or non-essential data is deleted, and the remaining data is processed to meet standardization, deduplication, verification, and ranking rules.
- Data Transfer: After the data has been transformed, it is shared in one or more clouds and then redistributed to appropriate target systems.
A data pipeline allows for the automation of all these steps in an intelligible, coherent way, with the aim of ensuring data security and facilitating smooth transfer of data.
Types of Data Pipelines Available
Below is an outline of the different types of data pipelines:
Batch
Batch pipelines are used to process data in batches. Batch processing is usually leveraged when a business wants to move high volumes of data at regular intervals. Batch processing jobs typically run on a fixed schedule (for instance, every 24 hours) or in some instances, once the volume of data reaches a given threshold. This process allows analysts to integrate large amounts of data and provide a reliable and fast decision model.
Streaming or Real-Time
These data pipelines are optimized to process millions of events at scale, in real-time. Because of this, you can gather, analyze, and store large amounts of information. Streaming/real-time pipelines are useful when processing data from a streaming source, such as telemetry from connected devices or data from financial markets.
Cloud
These pipelines are designed to work only with cloud-based data destinations, sources, or both. They are hosted directly in the cloud. As such they enable businesses to save money on expert resources and infrastructure.
Data Pipeline and ETL: Differences and Similarities
ETL and data pipeline are usually used interchangeably. ETL, which stands for Extract, Transform, and Load, is typically used to retrieve data from a source system, transform it depending on the requirements and load it into a data warehouse, mainly for analytical purposes. So what is a data pipeline? While it can be viewed as a broad term encompassing ETL as a subset, a data pipeline is a system that’s used to move data across systems. The data may or may not undergo any transformations. It may also be processed in real-time or in batches depending on a business and data needs. This data may be loaded into several destinations such as Data Lake and AWS S3 Bucket, or it might even be used to trigger a Webhook on a different system to begin a specific business process. In a nutshell, while both are terms for processes by which data moves from point A to point B, the key differences between data pipeline and ETL include:
- A data pipeline is an umbrella term of which ETL pipelines are a subset
- ETL pipelines always involve transformation, while the same isn’t true for data pipelines
- ETL pipelines run in batches, while data pipelines may run in real-time or in batches
How to Build an Efficient Data Pipeline for Your Business
When you think of technological solutions that power a successful business, a data pipeline isn’t always at the top of the list. This is because, although most forward-thinking businesses now realize that data is one of their most valuable assets, they still underestimate the importance of data engineering. Yet data pipelines can enable your business to unlock the data within your organization. With a data pipeline, you will be able to extract data from its source, transform it into a readable form, and load it into your systems, where you can use it to make insightful decisions. So what do you need to build a data pipeline?
Infrastructure
Many tools can be used for a data pipeline. The tool you use will depend on the project requirements, the data type, and objectives, among other factors. Some of the main tools needed include:
- Storage: Before data is processed and transferred, it needs to be collected. This can be done in a data lake, which is a storage repository used to store raw relational or non-relational data. Alternatively, it can be stored in a data warehouse—central repositories used to store historical and relational data.
- Batch scheduling software: The volume of data and information being processed continues to grow as businesses increase their digital initiatives. Batch scheduling software helps streamline automated data processing by providing capabilities and tools that eliminate manual intervention.
- ETL tools: These tools enable data integration strategies by allowing businesses to collect data from multiple sources and consolidate them into a single central location. A typical ETL process gathers and refines different types of data, then delivers the data to a data warehouse or a data lake.
Real-time data streaming tools: These tools analyze large amounts of data when they are used or produced. As such, real-time data streaming tools extract valuable information for the organization as soon as it’s produced or stored.
Strategy
Here are some of the things to consider when building a strategy for your data pipeline:
- Origin of the data: Origin is the point of entry of all data sources in a given pipeline. Most often, pipelines have IoT devices, application APIs, transactional processing applications, etc., or storage systems like data warehouses or data lakes as their origin.
- Destination: This refers to the final point of data transfer. The final destination usually depends on the use case. For most use cases, the destination is usually a data lake, data warehouse, or data analysis and business intelligence tool.
- Data flow: This is the movement of data from the origin to the final destination, along with the transformations that are performed on the data. While ETL is the most prominent tool used for data flow, it’s not necessarily the only tool you need for your data flow.
- Workflow: This is a definition of the sequence of processes as well as their dependency on one another in the pipeline.
- Monitoring: The objective of monitoring is to make sure that the pipeline and all its stages are working properly and performing the required tasks.
- Performance: The performance will be impacted by the size of your data and the structure of your pipeline, among other factors. You have to know the size and structure of your data to choose the right tools. For instance, if your server isn’t powerful enough, your data could take longer than expected to go through the pipeline.
Build Your Data Pipeline With ANALYB
While you can build a data pipeline from the ground up, the process can be time-consuming, resource-demanding, and not to mention challenging. Fortunately, you don’t have to go through all that trouble. ANALYB provides you with everything you need to build a data pipeline. These include:
- An ETL/ Data management services: To clean, combine, and transform data so that you can create complete and meaningful dashboards.
- A data warehouse: You can bring all your data into a central place to ensure consistency, data quality, and ease of reporting.
- A visualization tool for end-users: A drag and drop dashboard feature that enables you to transform raw data into insights quickly.